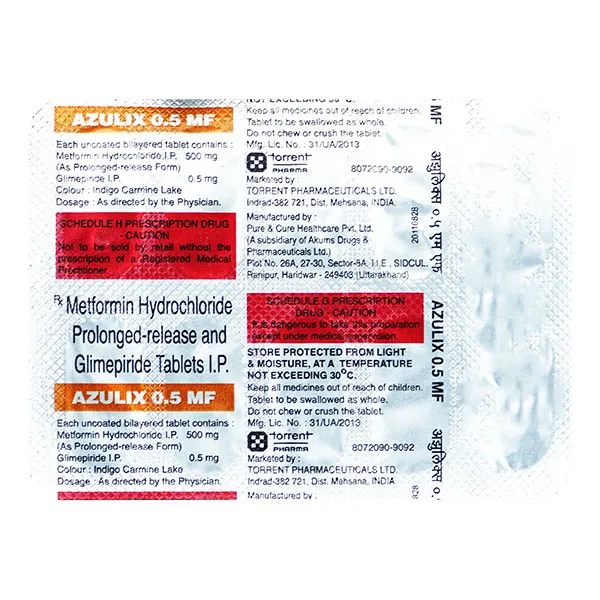
Use:
This drug belongs to a group of medicines called anti-diabetes drugs. It’s a mix of two drugs used to treat adults with type 2 diabetic mellitus. It helps manage blood glucose levels in diabetics.
Indication:
It should be taken in conjunction with food. To get the most out of it, it should be taken at a regular time each day. The dose of this medicine will be determined by your doctor and may vary depending on how it works with your blood sugar level.
It is important to continue taking this medicine even if you are feeling good or have your blood sugar under control. Stopping it without talking to your doctor could lead to an increase in your blood sugar, which could result in kidney damage or blindness, nerve damage, and even limb loss.
This is just one part of a comprehensive treatment plan that should include a nutritious diet, regular physical activity, and weight loss according to your doctor’s instructions. Your lifestyle is an important factor in managing diabetes.
Side Effects:
The most frequent side effect is hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). It is important to be aware of the symptoms of hypoglycemia, such as perspiration, dizziness, headaches, and tremors. It is also important to know how to manage hypoglycemia. The best way to avoid hypoglycemia is to eat regularly and always bring a fast-acting glucose source with you, such as sugary foods or fruit juice. Alcohol consumption can also increase the risk of hypoglycaemia, so it is best to avoid it. Other side effects of this medicine include: Taste changes, Nausea, Diarrhoea, Stomach pain, Headache, Upper respiratory tract infection. Some people find that they gain weight with this.
Safety Advice:
It may not be suitable for you if you have: type 1 diabetes mellitus, diabetic ketoacidosis, severe kidney or liver disease,heart disease, pregnant or breastfeeding, blood sugar levels should be monitored on a regular basis. your doctor may recommend blood tests to check your blood cell count and liver function.